Introduction
As people become more conscious of the importance of indoor air quality, dehumidifiers have become essential in homes and offices. They come in various shapes and sizes, utilizing different technologies to combat humidity. One emerging trend is the use of small semiconductor dehumidifiers, which promise efficient performance in a compact package. This article will explore how these devices work and compare their features with other types of dehumidifiers on the market.
The Basics: What is a Dehumidifier?
Before delving into semiconductor-based models, it’s crucial to understand what a dehumidifier does. These appliances remove excess moisture from the air, making indoor environments more comfortable and less conducive to the growth of mold and mildew. Traditional dehumidifiers often use a compressor and refrigerant to chill air, causing moisture to condense and collect in a reservoir.
How Do Small Semiconductor Dehumidifiers Work?
Semiconductor dehumidifiers utilize a different technology to remove moisture from the air. They employ a Peltier element—a semiconductor module that creates a temperature differential across two surfaces when an electric current passes through it.
Here’s a step-by-step explanation of the process:
- Air Intake: A fan draws humid air into the device.
- Cooling Process: The Peltier element cools one of its surfaces while heating the other.
- Condensation: Moist air flows over the cold surface, causing water vapor to condense.
- Collection: The condensed water collects in a reservoir.
- Exhaust: The dry air is expelled back into the room.
Here’s an image from the Makayla website:
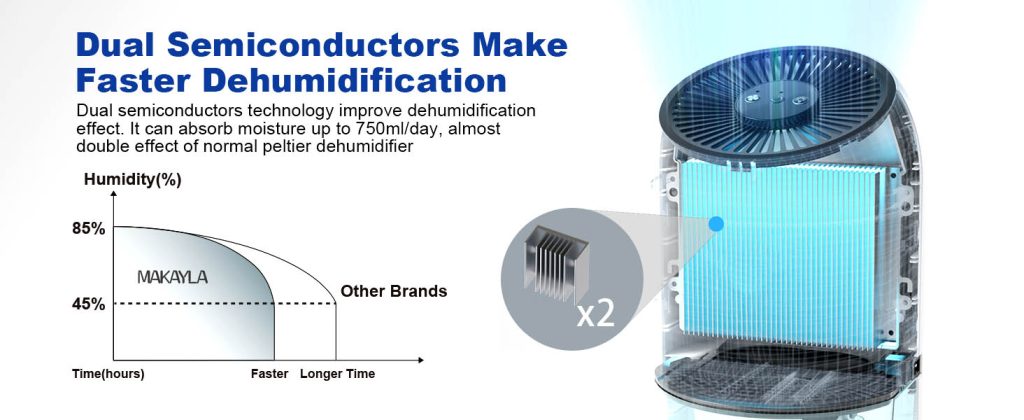
Here is a video of the inner workings of a small dehumidifier
Advantages of Semiconductor Dehumidifiers
Energy Efficiency
Semiconductor dehumidifiers often consume less power than traditional compressor-based systems, making them more energy-efficient for small spaces.
Quiet Operation
They operate silently due to the lack of mechanical parts like compressors and evaporators, which is a significant advantage in noise-sensitive environments like bedrooms and offices.
Portability
Their compact size and lightweight nature make them portable and easy to place in various locations.
Drawbacks
Limited Capacity
Because they are small, semiconductor dehumidifiers usually have a lower moisture removal capacity compared to larger units.
Ineffectiveness in Large Spaces
These devices are not ideal for large areas or highly humid conditions, as their moisture removal rate is relatively slow.
Comparison with Other Types
Compressor-Based Dehumidifiers
- Efficiency: Less energy-efficient than semiconductor models but more effective in large spaces.
- Noise: Generally louder due to the compressor and fan operations.
- Capacity: Typically higher moisture removal capacity.
Desiccant Dehumidifiers
- Efficiency: Often less energy-efficient than both compressor and semiconductor types.
- Noise: Quiet but not as silent as semiconductor models.
- Capacity: Varies, but generally effective in both small and large spaces.
Small semiconductor dehumidifiers offer a unique combination of features that make them ideal for certain applications, such as small rooms and quiet environments. However, they are not a one-size-fits-all solution. Compressor-based and desiccant dehumidifiers still hold advantages in terms of moisture removal capacity and effectiveness in larger spaces. Choosing the right dehumidifier ultimately depends on your specific needs, including the size of the area you wish to dehumidify, noise tolerance, and energy efficiency requirements.
Our Favorite Pick for Small Dehumidifiers

Hi, I’m Cohan, the author behind Your Dehumidifier Guide, a website dedicated to helping you create a healthier and more comfortable living environment. With a tagline of “Breathe Easy, Live Better,” my ultimate goal is to provide you with the best dehumidification solutions for your home. Whether you’re looking for the perfect dehumidifier for your bathroom, small room, or basement, I’ve got you covered. Through in-depth reviews and comprehensive buying guides, I aim to equip you with the knowledge to tackle high humidity levels, prevent mold growth, and improve your indoor air quality. Trust me to be your ultimate guide in the world of dehumidifiers.